

When an electron enters a region in which there is a uniform magnetic field, B, perpendicular to the velocity, v, of the electron (Caution: The capital letter V will be. The currently accepted value for e / m is 1.758820 × 10 11 C/kg. Conductivity is proportional to the product of mobility and carrier concentration. At standard temperature and pressure two atoms of the element bond to form N 2 a. In this experiment you will measure e/m, the ratio of the charge of an electron to the mass of an electron. Electron mobility is almost always specified in units of cm 2 /(Vs).This is different from the SI unit of mobility, m 2 /(Vs).They are related by 1 m 2 /(Vs) 10 4 cm 2 /(Vs). WeĪlso discuss the important issues of read-out of single-electron events and What is the ionic charge of an ion with 13 protons and 10 electrons. Still often potentially competitive if technical constraints can be lifted. Needs, in terms of transfer errors and transfer rate, of quantum metrology ofĮlectrical quantities, whereas some others are currently "just" wild ideas, Some of them have already proven experimentally to nearly fulfill the demanding We then present the broad variety of proposed realizations. In this review we firstĭiscuss the generic physical phenomena and technical constraints that influenceĬharge transport. Ever since, producing anĮlectrical current $ef$, or its integer multiple, at a drive frequency $f$ hasīeen in a focus of research for metrological purposes.
#Standard charge of electron pdf#
Pekola and 6 other authors Download PDF Abstract: Controlling electrons at the level of elementary charge $e$ has beenĭemonstrated experimentally already in the 1980's. Lett., 75 (20): 3598–3601, Bibcode: 1995PhRvL.75.3598F, doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.Download a PDF of the paper titled Single-electron current sources: towards a refined definition of ampere, by J. (1995), "Determination of the Electron's Atomic Mass and the Proton/Electron Mass Ratio via Penning Trap Mass Spectroscopy", Phys. ^ a b The NIST reference on Constants, Units, and Uncertainty, National Institute of Standards and Technology, 10 June 2009.

The NIST Reference on Constants, Units and Uncertainty. In the experiment P6.1.3.1, a tightly bundled electron beam is diverted into a closed circular path using a homogeneous magnetic field in order to determine. ^ a b c "CODATA Value: electron mass".
The NIST Reference on Constants, Units, and Uncertainty.

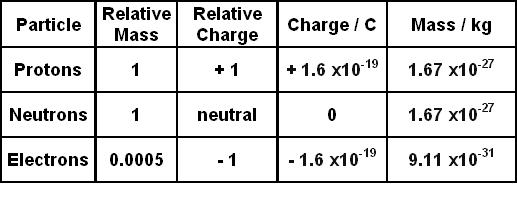
Most practical measurements are carried out on moving electrons. The term "rest mass" is sometimes used because in special relativity the mass of an object can be said to increase in a frame of reference that is moving relative to that object (or if the object is moving in a given frame of reference). Once all of the values were found the equation e/m2V/B2r2 to calculate the electron charge to mass ratio, which was calculated to be 3.24x1011C/kg. The r value for ring number three 7.5x103m. It has a value of about 9.109 ×10 −31 kilograms or about 5.486 ×10 −4 daltons, which has an energy-equivalent of about 8.187 ×10 −14 joules or about 0.511 MeV. The next step in the experiment was the radius for the electron beam, to do this the equation r(.25x10-2m)(ring number) was used. It is one of the fundamental constants of physics. In particle physics, the electron mass (symbol: m e) is the mass of a stationary electron, also known as the invariant mass of the electron.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
